Tube Inspection Services
Tubes in Heat Exchangers, Air Fin Coolers and Boilers are often causes of concern as they are subject to process
chemistry on both sidesor to process chemistry on one side and water / steam / atmosphere on the other.
Chemical Fluid and Heat Transfer contribute to accelerated corrosion of tube materials.
Failure of these components can result in various consequences that include
- Explosion / Loss of Lives!
- Unexpected shutdown of unit/ plant resulting in Production losses
- Additional cost for Emergency Repair / action to be undertaken
Very often closer one is to Failure - Direct Effects Become Apparent. Cumulative effects of Failure are very often overlooked in the rush to fix the problem. Too often cause of failure is ignored / forgotten due to time constraints and Failure or Corrosion is considered " Just Cost of Doing Business ".
Invariably, such problems become chronic and associated costs, tribulations and delays become ingrained. Problems persist until cost or concern overwhelm corporate inertia. Temporary Solution becomes no longer acceptable. Correct Solution is to Identify and Eliminate the Failure.
With the right inspection technique and tools, these situations can be avoided as preventative costs are almost always a small fraction of those associated with neglect.
ESCON offers Eddy Current Testing (ECT), Remote Field Eddy current Testing ( RFET), Near Field eddy current Testing ( NFT), Magnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) Testing and Ultrasonic IRIS as inspection choices for the inspection of Heat Exchanger, Air Fin Cooler and Boiler Tubes.



Heat Exchanger Tube Inspection
Know About Your Heat Exchanger Tube Problems Long Before They Cost You!!!

Heat Exchangers are critical components in any chemical processing operation. Tubes in these units are subject to process chemistry on both sides or to process chemistry on one side and water or steam on the other. The chemical fluids flowing through these tubes and heat transfer conditions contribute to accelerated corrosion of tube materials
The commonly used techniques to inspect Heat Exchanger tubes include :
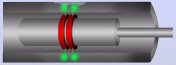
ECT
Eddy Current Technique
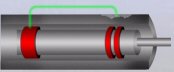
RFEC/RFET
Remote Field Eddy Current Technique

NFT
Near Field Eddy Current Technique

MFL
Magnetic Flux Leakage Technique
Magnetic Flux Leakage Technique

IRIS
Ultrasonic Internal Rotating Inspection System
Each of these inspection techniques has its own merits and demerits
Over the years with shrinking maintenance budgets and longer intervals between plant shutdowns the need for reliable inspection of these units has increased. With the advent of digital processing technology, several enhancements to the inspection equipment have taken place.
While developing an Inspection Program for Heat Exchangers, the following parameters need to be considered:
- The presence of advanced techniques alone is not enough to provide reliable solutions for Heat exchanger tube inspection.
- No single technique can be used as a one stop solution for all corrosion problems.
- Proper understanding of the inspection techniques and knowing their advantages and limitations is very important. Sufficient knowledge of corrosion mechanisms in Heat Exchangers plays a crucial role in deriving proper inspection methodologies.
At ESCON, we have a wide range of equipment based on various techniques and experience of inspecting over 5000 Heat Exchangers, 500,000 tubes with several validated results.
Air Fin Cooler Tube Inspection
Inspection of Air Fin Coolers is slightly more complex than normal Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers.This is due to the presence of Aluminium Fins on the tube external.
Non-Ferromagnetic Tubes are inspected using the Eddy Current Technique (ECT) or Ultrasonic IRIS. The application of ECT for non-ferrous tubes depends on the way the fins are attached to the tubes.
Ferromagnetic Tubes are quickly screened for defects with Near Field Eddy Current TechniMagnetic Flux Leakage (MFL) techniques and the results are cross-verified with Ultrasonic IRIS.
When tube corrosion occurs on the unfinned area close to the header box, it is advisable to only employ the Ultrasonic IRIS technique.

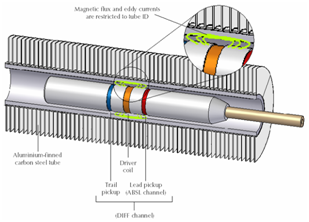
NFT
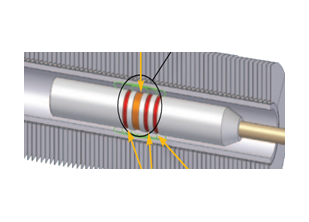
MFL

IRIS
Boiler Tube Inspection
Boilers are key equipment in all plants. Failure of tubes in Boilers as seen in the pictures below can have devastating effects on plant operation and safety as well. Corrosion and wall thinning in Boiler tubes occur due to several factors. Their detection and sizing can be achieved using a wide range of inspection tools, common among which are the following :

RFEC / RFET
Remote Field Electromagnetic Testing
RFET can be applied using a probe inserted into the tube. Smaller sized probes are used that are flexible and can encounter bends. Sensitivity to small flaws is low and also has problems in sizing flaws at bends.

IRIS
Ultrasonic Internal Rotating Inspection System
IRIS can be applied only to straight sections of the tube using cables that can pass through bends. It provides valuable information of tube thickness and also a profile of the defects if any in the tube


While developing an Inspection Program for Boilers, the following parameters need to be considered:
- The nature of corrosion anticipated plays a crucial role in determining the choice of technique to be deployed as no single technique can be used as a one stop solution for all corrosion problems.
- The geometry of the tubes and inspection access also restricts the usage of certain techniques.
- Proper understanding of the inspection techniques and knowing their advantages and limitations is very important.